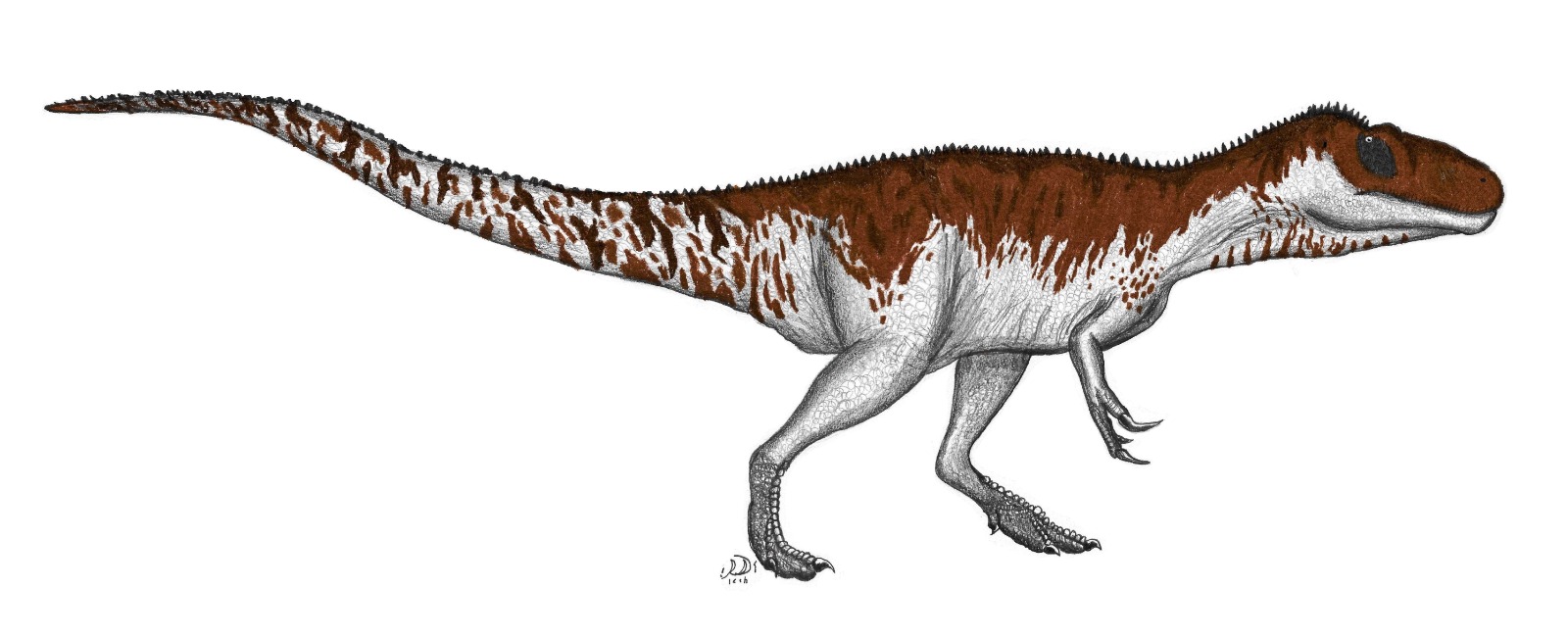
Afrovenator was an efficient bipedal predator. With a length of 9 meters and a height of 3.5 meters, it was a dangerous hunter that pursued and devoured herbivorous dinosaurs like Jobaria, whose fossils were found in the same rock formations.
It possessed a graceful build with long, slender legs and a long, balancing tail.
Its serrated teeth, about 5 cm long, were excellent for cutting deep into the flesh of its victims and tearing them from the body.
It possessed long sickle claws on three fingers with which it could grasp and probably slash its prey.
To date, Afrovenator is the most complete Cretaceous predatory dinosaur fossil ever found in Africa.
The blueprint of its body suggests that it was a cousin of Allosaurus, a 150-million-year-old dinosaur from North America.
However, it was probably lighter and more light-footed than Allosaurus, as indicated by its longer and slimmer bones.
Afrovenator's fossil remains were discovered in 1993 by paleontologist Paul Sereno and his team in North Africa's Niger Republic.
The name Afrovenator abakensis means as much as the hunter from Avatar, Africa. The species name abakensis was given to the dinosaur because of the place where its skeleton was found in the Sahara region of Agadez. This is because Abaka is the Touareg name for this region in Niger.
The skeleton found by Sereno was more complete than any previously discovered Cretaceous African carnivore.
| Profile | Afrovenator |
|---|---|
| Prehistoric Era | Middle Jurassic to ? Upper Jurassic 168 to ? 157 million years |
| Order | Saurischia |
| Suborder | Theropoda |
| Family | Megalosauridae |
| Tribe | |
| Genus | Afrovenator |
| Species | Afrovenator abakensis |
| Height | 3.5 meter |
| Length | 7 to 9 meter |
| Weight | 1 ton |
| Territory | Tiouraren Formation, Agadez, Niger |
The area where Afrovenator lived was lushly forested with nearby lakes and rivers.
As mentioned above, a large sauropod named Jobaria tiguidensis was found in the same formation where Afrovenator was found.
Scientists suspect that Afrovenator hunted this sauropod. Since Jobaria tiguidensis grew to be 18 to 21 meters long, it is likely that it targeted the smaller juveniles in particular, as the smaller specimens would have been easier for a predator the size of Afrovenator to handle. However, there is no scientific evidence for this thesis so far.
Because of its similarity to Allosaurus, it is speculated that Afrovenator lived in packs and even hunted adult specimens of Jobaria.
Currently Afrovenator is assigned to the family Megalosauridae.
Paul Sereno, who first described Afrovenator in 1994, assigned it to the Torvosauroidea. Sereno came to this assumption because the rock layer from which the fossil was recovered was assigned to the Early Cretaceous. In the meantime, the rock layers have been re-dated and assigned to the Middle Jurassic.
Another 2003 study by Rauhut sees Afrovenator not as a member of the Megalosauroidea but as a close relative of Allosaurus.
However, the official affiliation is currently to the family Megalosauridae.
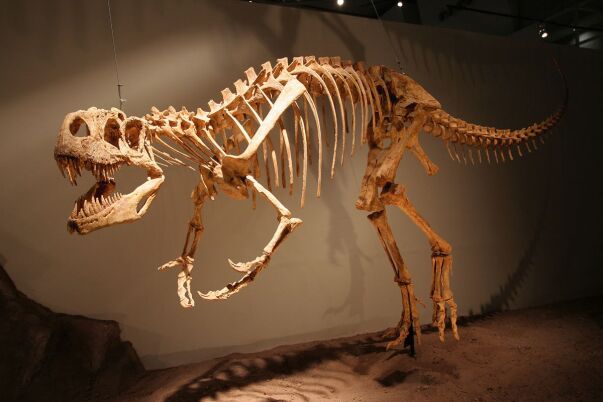

Image source:PaleoGeekSquared, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Skeleton: Kabacchi, CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Skeleton (2): Jaime Headden (User:Qilong), CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Size: PaleoGeekSquared, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Commons